Where Are Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Editor’s note: At a time when potentially risky energy storage technologies can be found in everything from consumer products to transportation and grid storage, UL Research Institutes helps to lay the groundwork for energy storage designs that are safe and reliable. As part of our work in this field, we want to share information on the foundations and current landscape of electrochemical safety.
How common are lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are used in a wide variety of applications ranging from wearable technology and mobile phones to satellites and electric buses. Lithium-ion is the most popular rechargeable battery chemistry used today.
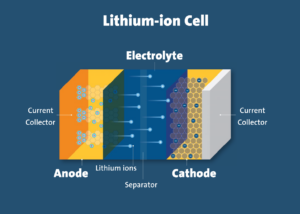
The products powered by lithium-ion batteries require a range of specifications for optimum and safe performance with respect to energy, power and life span. Lithium-ion batteries and cells are produced in a variety of chemistries and shapes, also known as formats.
How are lithium-ion batteries used?
Applications of lithium-ion batteries include:
- Mobile phones
- Laptops and tablets
- Wearable technology such as wireless headphones and smart watches
- Electric vehicles including automobiles, buses, rail, bicycles, scooters and hoverboards
- Portable and stationary power banks
- Renewable energy storage
- Implanted medical devices
- Cordless power tools
- Drones
- Satellites
Why are lithium-ion batteries so prevalent?
Lithium-ion batteries offer a number of benefits that make them well-suited to energy storage for a wide range of applications. Some of these benefits include:
- High energy density: Lithium-ion batteries can store a large amount of energy in a small volume and can be very light.
- High power density: Lithium-ion batteries have the capability to support very high power demands.
- Rechargeability: Lithium-ion batteries can be charged hundreds to thousands of times.
- Portability: The combination of high energy density and rechargeability makes lithium-ion batteries useful for powering portable devices.
PUBLISHED