What Is Thermal Runaway?
Editor’s note: At a time when potentially risky energy storage technologies can be found in everything from consumer products to transportation and grid storage, UL Research Institutes helps to lay the groundwork for energy storage designs that are safe and reliable. As part of our work in this field, we want to share information on the foundations and current landscape of electrochemical safety.
What is thermal runaway?
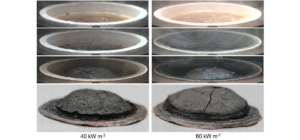
Thermal runaway is one of the primary risks related to lithium-ion batteries. It is a phenomenon in which the lithium-ion cell enters an uncontrollable, self-heating state.
Thermal runaway can result in:
- Ejection of gas, shrapnel and/or particulates (violent cell venting)
- Extremely high temperatures
- Smoke
- Fire
Is it normal for lithium-ion cells to produce heat?
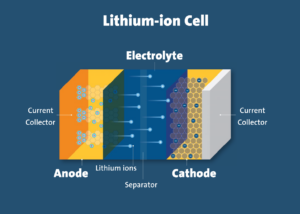
In lithium-ion cells, the movement of electrons and lithium ions produces electricity. The process of charge and discharge is normally accompanied by a small amount of heat.
In ideal conditions, the heat is able to dissipate from the cell. However, in thermal runaway, the lithium-ion cell generates heat at a rate several times higher than the rate at which heat dissipates from the cell.
The cell reaches thermal runaway when its temperature rises uncontrollably at a rate greater than 20° centigrade per minute with maximum temperatures reaching greater than 300°C accompanied by gas and/or electrolyte venting, smoke or fire or a combination of all.
Learn more about what causes thermal runaway.
What is lithium-ion?
Consisting of single or multiple lithium-ion cells along with a protective circuit board, lithium-ion is the most popular chemistry used in rechargeable batteries today.
What are lithium-ion batteries?
Learn more about the lithium-ion batteries that power the devices we use every day, like our mobile phones and electric vehicles.
PUBLISHED