Paving the Way for Green Hydrogen Energy
Green hydrogen technology holds great promise for sustainable energy. A carbon-free energy carrier produced from water and renewable energy sources, green hydrogen has the potential to decarbonize multiple sectors, including transportation and shipping industries, global energy markets, and industrial sectors. Still, green hydrogen technology faces several development bottlenecks — the high cost of large-scale hydrogen production; bulk storage, transport, and distribution issues; and safety concerns, among others.
The Electrochemical Safety Research Institute (ESRI) is working to break through those bottlenecks. In June 2022, ESRI launched a collaborative research effort with University of Houston‘s (UH) Dr. Xiaonan Shan to develop new materials and methods for producing hydrogen. The project also calls for characterizing the safety of hydrogen energy at all stages.

“The safety of green hydrogen during production, storage, transportation and use has not been explored,” said Dr. Judy Jeevarajan, vice president and executive director of ESRI. “Our interest is to be proactive in this understanding before hydrogen becomes a fuel, especially in electric vehicle applications.”
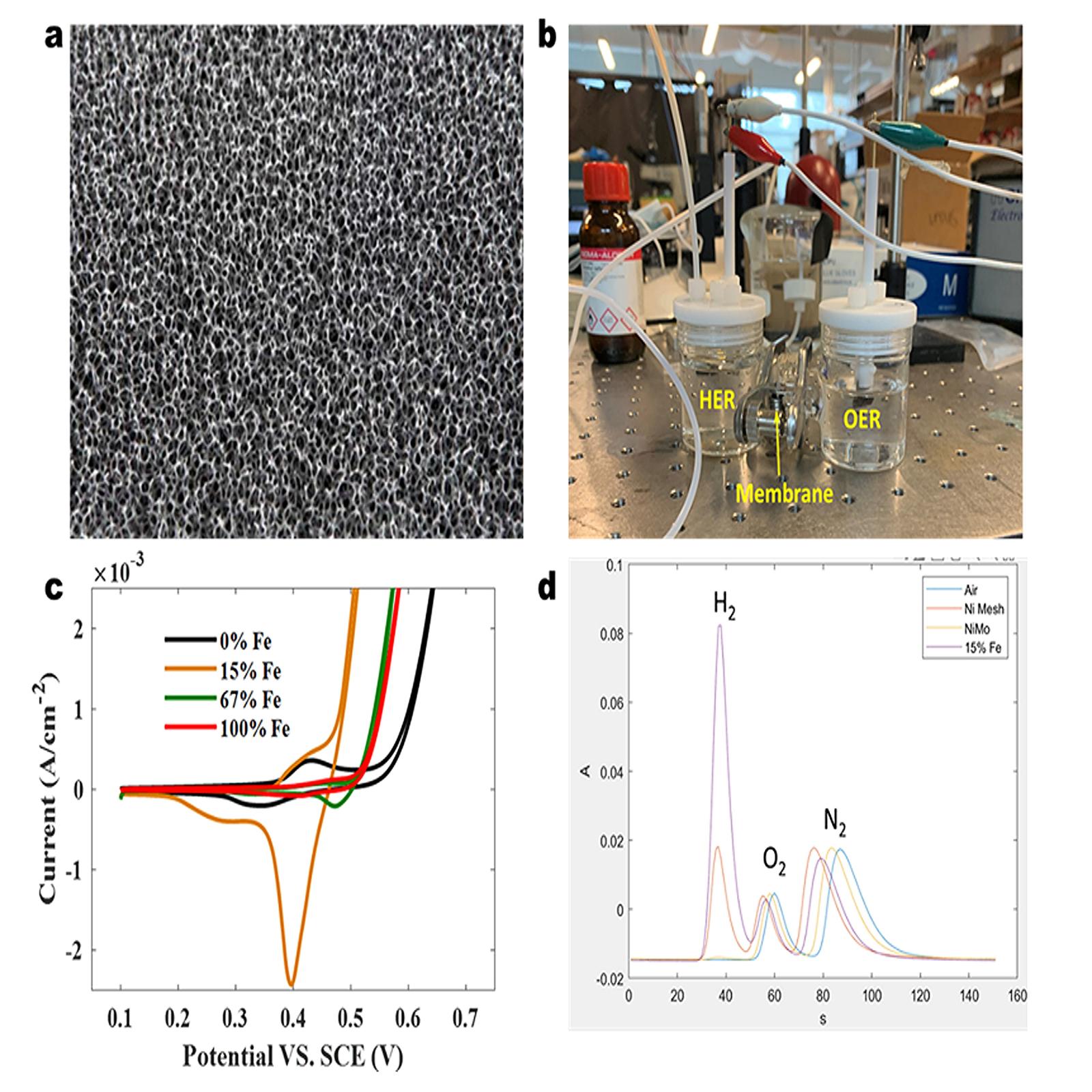
The ESRI-UH team aims to find materials that can replace platinum cathode and iridium oxide anode electrodes used in producing hydrogen. Team members are investigating the impact of electrode surface area, morphology, and current density on the hydrogen production rate and longevity.
As part of this effort, ESRI is also looking into creating new materials capable of producing green hydrogen using low-temperature electrolysis (LTE), which comprises three different technologies:
- Liquid alkaline systems
- Proton exchange membrane or polymer electrolyte membrane systems
- Anion exchange membrane or alkaline electrolyte membrane systems
Studies will focus on investigating the impact of distance between the cathode and anode and the current density on the hydrogen and oxygen evaluation reaction.

Revolutionizing Safety Through Science
At UL Research Institutes, we tackle tough issues with a scientific rigor trusted throughout the world.
PUBLISHED









